Women's health is one of the most important issues that should be protected through regular gynecological check-ups. During these examinations, certain tests play a vital role in the early diagnosis of cervical diseases. Colposcopy is one of the most detailed and reliable of these tests. Especially when an abnormality is detected in the Pap smear test or an HPV infection is identified, the colposcopy procedure is recommended by doctors. Through this procedure, the cervix, vagina, and vulva tissues are magnified and examined, allowing possible diseases to be detected at an early stage.
What Is Colposcopy?
Colposcopy is a diagnostic procedure performed by gynecologists to examine the cervix, vagina, and vulva tissues in detail. During this procedure, a special microscope called a “colposcope” is used. The colposcope is a lighted and magnifying device that allows the doctor to see cellular changes that cannot be detected with the naked eye more clearly.
Colposcopy is usually performed when abnormal cells are found in a Pap smear test. This test is extremely important for the early detection of precancerous lesions of the cervix. In addition, colposcopy is also preferred to examine possible changes in the cervix of women diagnosed with HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) infection.
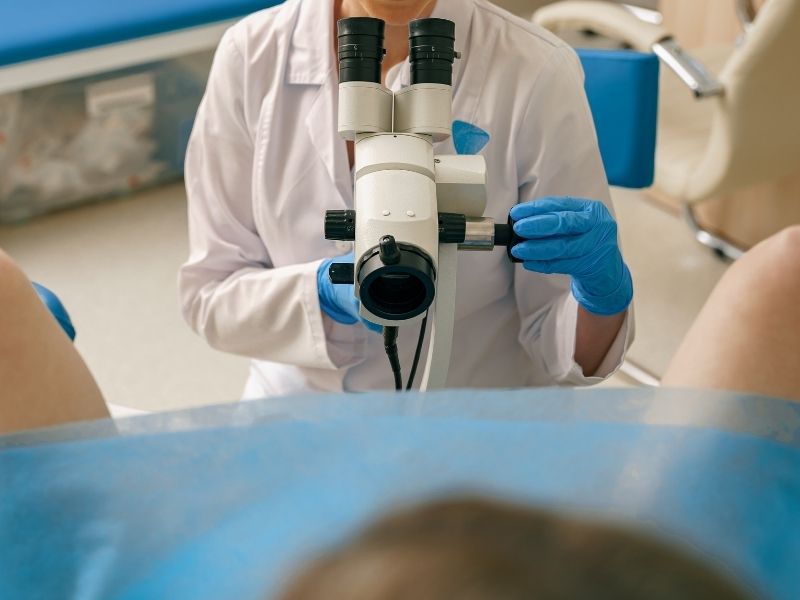
This method is a painless procedure and allows the patient to easily return to daily life. Colposcopy is one of the most effective early diagnostic methods used to reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
Why Is Colposcopy Performed?
The colposcopy procedure is generally performed when unusual results are obtained in a Pap smear test. If the Pap smear result reports cellular abnormalities such as “ASCUS,” “LSIL,” or “HSIL,” the doctor may recommend colposcopy.
The main purposes of performing this procedure are as follows:
To detect cellular changes that may lead to cervical cancer, to observe the damage caused by HPV infection on the cervix, to understand the cause of lesions that occur in the vagina or vulva, to identify the source of unexplained vaginal bleeding, and to make an accurate diagnosis before treatment. In addition, colposcopy can also be performed during pregnancy to evaluate the condition of the cervical tissues. The biopsy samples taken during this procedure are highly valuable in detecting the presence of precancerous or cancerous cells.
How to Prepare for a Colposcopy
There are several important points that patients should pay attention to before undergoing a colposcopy. These preparations help ensure that the procedure is completed comfortably and with accurate results.
First of all, it is recommended to avoid vaginal douching, tampon use, or sexual intercourse for at least 24 hours before the procedure. This helps maintain the natural condition of the vaginal environment. In addition, performing colposcopy during menstruation is generally not preferred; the ideal time is a few days after the period has ended.
The doctor provides detailed information to the patient about what to expect before the procedure. On the day of the procedure, the patient should wear comfortable clothing and try to stay as relaxed as possible. Any medication use or allergies should be reported to the doctor.
How Is Colposcopy Performed?
The colposcopy procedure usually takes between 10 and 20 minutes and does not require local anesthesia. The patient lies on the examination table in a gynecological position. The doctor inserts an instrument called a speculum into the vagina, allowing the cervix to be clearly visible.
Then, the colposcope device is positioned outside the vagina and directed toward the cervix. Thanks to the magnification feature of the colposcope, the doctor can examine the vascular structure, color changes, and surface abnormalities of the cervix in detail.
A special solution (usually acetic acid or Lugol’s solution) is applied to the cervix. This solution causes abnormal cells to turn white, making potential lesion areas easier to identify. If a suspicious area is detected, the doctor may take a biopsy. This biopsy procedure may cause a brief mild stinging sensation but is generally painless.
The biopsy sample is sent to the laboratory, and the results are evaluated within a few days. After the procedure, the patient can return to normal daily activities the same day.
What Should Be Considered After a Colposcopy?
After a colposcopy, light vaginal discharge or spotting is normal. This condition usually resolves on its own within a few days. For the first 48 hours following the procedure, vaginal douching, tampon use, and sexual intercourse are not recommended. This period allows the cervical tissues to heal properly.
If pain occurs, mild pain relievers recommended by the doctor can be used. However, if severe pain, foul-smelling discharge, or heavy bleeding develops, the doctor should be contacted immediately.
Colposcopy results are usually available within a few days. Based on the results, the doctor may order additional tests or create a treatment plan if necessary. Regular follow-ups and check-ups are extremely important for maintaining cervical health.
What Are the Advantages of the Colposcopy Procedure?
The colposcopy procedure offers many important advantages for women’s health. Its greatest benefit is the ability to detect precancerous cellular changes in the cervix at an early stage. This allows serious diseases to be treated before they progress.
In addition, colposcopy is a painless and safe procedure. It is completed in a short time without the need for surgery. At the same time, it enables the doctor to directly observe the cervical tissue, which increases diagnostic accuracy.
Another advantage is that the biopsy samples taken during colposcopy can be examined in detail. This helps determine the degree of possible precancerous changes and allows for the preparation of an appropriate treatment plan.
Colposcopy plays a vital role in early diagnosis, especially in individuals who test positive for HPV. Regular gynecological check-ups and timely procedures like this help women maintain their quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Colposcopy Is Performed
Which Doctor Performs a Colposcopy?
The colposcopy procedure is performed by a gynecologist (specialist in obstetrics and gynecology). These specialists are trained to examine the cervix and vaginal tissues.
Is Colposcopy a Painful Procedure?
Colposcopy is generally a painless procedure. Some patients may feel a slight sting or cramp if a biopsy is taken, but this is usually brief and does not require local anesthesia.
Can Colposcopy Be Done During Menstruation?
No. Performing colposcopy during menstruation makes it difficult to see the cervix clearly. Therefore, the procedure should be done a few days after the end of the period.
When Are Colposcopy Results Available?
If no biopsy is taken, the results are usually evaluated the same day. If a biopsy is performed, the pathology report is ready within 5–10 days, and the doctor provides guidance based on the results.
Can Colposcopy Be Performed During Pregnancy?
Yes, colposcopy can be safely performed during pregnancy. However, if a biopsy is necessary, the doctor makes this decision carefully to avoid any harm to the baby.
Is Anesthesia Required for Colposcopy?
Anesthesia is generally not required. The procedure is short and causes minimal discomfort. However, in patients with high sensitivity, a local anesthetic spray may be used.
When Can You Shower After Colposcopy?
You can take a shower the same day after the procedure, but vaginal douching should be avoided as it may increase the risk of infection and delay healing.
Can You Exercise After Colposcopy?
Light exercise is allowed, but it is recommended to avoid intense physical activity for the first 48 hours after the procedure. This helps prevent bleeding and discomfort.
Does Colposcopy Affect Sexual Activity?
It is generally recommended to avoid sexual intercourse for 2–3 days after colposcopy. This allows the cervix to heal completely.
What Happens If the Colposcopy Report Shows Abnormalities?
If abnormal cell changes are detected in the report, the doctor may recommend additional tests (such as biopsy, HPV typing, or LEEP procedure). This is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment of the condition.